
Radial head fractures may be difficult to visualize on initial imaging but should be suspected when there are limitations of elbow extension and supination following trauma.
Greenstick fracture how to#
Combined fractures involving both the ulna and radius generally require surgical correction. Missed Greenstick Fracture Claims Guide How To Claim Compensation For A Misdiagnosed Greenstick Fracture Did you suffer avoidable harm when you had a missed. After assessing the nature of the injury, an orthopedic doctor may recommend several recovery strategies. If any warning signs of a greenstick fracture present, immediate orthopedic treatment is mandatory, as a broken bone that does not receive appropriate care may heal in a deformed manner. These fractures are treated with immobilization or surgery, depending on the degree of displacement and angulation. How Orthopedists Treat Greenstick Fractures. Huge collection, amazing choice, 100+ million high quality, affordable RF and RM images. Isolated midshaft ulna (nightstick) fractures are often caused by a direct blow to the forearm. Find the perfect greenstick fracture stock photo. A bicortical fracture occurs when the bone breaks completely.
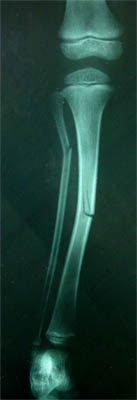
It should be noted that these fractures may be complicated by a median nerve injury. There are two types of radial shaft fractures: bicortical fractures and greenstick fractures. Greenstick fractures occur most often during infancy and. A greenstick fracture occurs when a bone bends and cracks, but doesn’t break all the way like what happens when you bend a green stick of wood. A nondisplaced, or minimally displaced, distal radius fracture is initially treated with a sugar-tong splint, followed by a short-arm cast for a minimum of three weeks. A greenstick fracture is a fracture in a young, soft bone in which the bone bends and breaks. Greenstick fractures have a high risk of breaking completely through the bone, so most of these types of fractures are immobilized in a cast during healing. In adults, distal radius fractures are the most common forearm fractures and are typically caused by a fall onto an outstretched hand. Depending on the degree of angulation, buckle and greenstick fractures can be managed with immobilization. Greenstick fractures, which have cortical disruption, are also common in children. Incomplete compression fractures without cortical disruption, called buckle (torus) fractures, are common in children. If initial imaging findings are negative and suspicion of fracture remains, splinting and repeat radiography in seven to 14 days should be performed. Evaluation with radiography or ultrasonography usually can confirm the diagnosis. A fall onto an outstretched hand is the most common mechanism of injury for fractures of the radius and ulna. Fractures of the radius and ulna are the most common fractures of the upper extremity, with distal fractures occurring more often than proximal fractures.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
